TikZ Figures
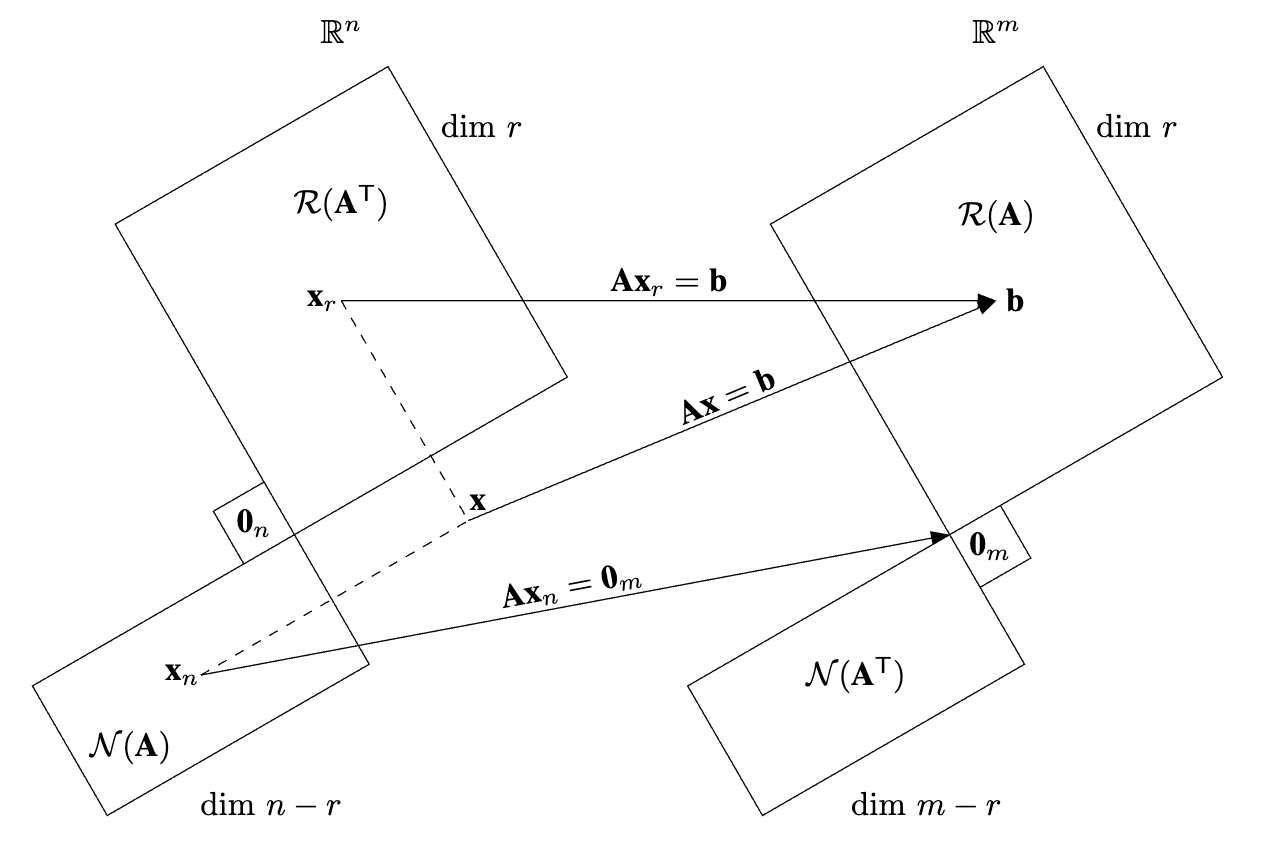
Subspaces
-
-
Required Math Formatting Packages:
\usepackage{amsmath} \usepackage{amssymb} \DeclareMathAlphabet{\mbf}{OT1}{ptm}{b}{n} \providecommand{\trans}{{\ensuremath{\mathsf{T}}}}Required Tikz Packages and Libraries:
\usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{positioning, arrows.meta, calc, intersections}TikZ Code:
\begin{tikzpicture} % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Required Tikz Libraries % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % \usetikzlibrary{positioning, arrows.meta, calc, intersections} % 1) arrows.meta is used for arrow tips % 2) positioning is used for relative positioning of nodes % 3) calc is used for coordinate calculations % 4) intersections is used to find the intersection of two paths % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Constant Dimension Parameters % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % \def\blockAngle{30} % Rotation of the block \def\blockAngleMirrored{\blockAngle + 90} % Mirror angle about x-axis \def\blockXshift{7} % Shift in x-direction \def\dashedLineAngle{\blockAngle - 90} % Angle of lines intersecting at x \def\dashedLineAngleMirrored{\blockAngle} % Angle of lines intersecting at x \def\arrowTipLength{2mm} % Length of arrow tip -> \def\arrowTipWidth{1.5mm} % Width of arrow tip -> \def\arrowTextYshift{2pt} % Shift text above the arrow \pgfmathsetmacro{\cosBlockAngle}{cos(\blockAngle)} % Trig for finding corners \pgfmathsetmacro{\sinBlockAngle}{sin(\blockAngle)} % Trig for finding corners % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Objects and Styles % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Setting custom arrow style (uses package arrows.meta) \tikzset{ myarrow/.style = {->, -{Triangle[length=\arrowTipLength, width=\arrowTipWidth]}} } % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Start Drawing the Diagram % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define the coordinates of the corners of the left space \coordinate (left_center) at (0, 0); \coordinate (xr_corner) at (1, 5); \coordinate (xn_corner) at (-2, -3); % Shift the coordinates to the right to make the right space \coordinate (right_center) at ($(left_center) + (\blockXshift, 0)$); \coordinate (b_corner) at ($(xr_corner) + (\blockXshift, 0)$); \coordinate (NAT_corner) at ($(xn_corner) + (\blockXshift, 0)$); % Draw the x_r space \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngle:(left_center)}] \draw (left_center) rectangle (xr_corner); \node at ($(left_center)!0.5!(xr_corner)$) (x_r_space) {}; \end{scope} % Draw the x_n space \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngleMirrored:(left_center)}] \draw (left_center) rectangle (xn_corner); \node at ($(left_center)!0.5!(xn_corner)$) (x_n_space) {}; \end{scope} % Draw the b space \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngle:(right_center)}] \draw (right_center) rectangle (b_corner); \node at ($(right_center)!0.5!(b_corner)$) (b_space) {}; \end{scope} % Draw the N(A') space \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngleMirrored:(right_center)}] \draw (right_center) rectangle (NAT_corner); \node at ($(right_center)!0.5!(NAT_corner)$) (NAT_space) {}; \end{scope} % Define the dashed paths to find the intersection point x \path[name path=path_r] (x_r_space.center) -- ++(\dashedLineAngle:5cm); \path[name path=path_n] (x_n_space.center) -- ++(\dashedLineAngleMirrored:5cm); % Find the intersection point x \path[name intersections={of=path_r and path_n, by=x}]; % Draw dashed lines up to the intersection point x \draw[dashed] (x_r_space.center) -- (x); \draw[dashed] (x_n_space.center) -- (x); % Draw the arrows \draw[myarrow] (x_r_space.center) -- (b_space.center) node[midway, sloped, above, yshift=-\arrowTextYshift] {$\mbf{A}\mbf{x}_{r} = \mbf{b}$}; \draw[myarrow] (x_n_space.center) -- (right_center.center) node[midway, sloped, above, yshift=-\arrowTextYshift] {$\mbf{A}\mbf{x}_{n} = \mbf{0}_{m}$}; \draw[myarrow] (x.center) -- (b_space.center) node[midway, sloped, above, yshift=-\arrowTextYshift] {$\mbf{A}\mbf{x} = \mbf{b}$}; % Label the Spaces \node[above=0.6cm of x_r_space] {$\mathcal{R}(\mbf{A}^{\trans})$}; \node[below=0.35cm of x_n_space, xshift=-0.75cm] {$\mathcal{N}(\mbf{A})$}; \node[above=0.47cm of b_space] {$\mathcal{R}(\mbf{A})$}; \node at (NAT_space) {$\mathcal{N}(\mbf{A}^{\trans})$}; \node at (x_r_space) [xshift=-0.2cm] {$\mbf{x}_{r}$}; \node at (x_n_space) [xshift=-0.2cm] {$\mbf{x}_{n}$}; \node at (b_space) [xshift=0.2cm] {$\mbf{b}$}; \node at (x) [xshift=0.1cm, yshift=0.2cm] {$\mbf{x}$}; \node[above=2.5cm of x_r_space, xshift=0cm] {$\mathbb{R}^{n}$}; \node[above=2.5cm of x_r_space, xshift=0cm + \blockXshift cm] {$\mathbb{R}^{m}$}; \node[above=1.5cm of x_r_space, xshift=1.5cm] {$\dim \, r$}; \node[above=1.5cm of x_r_space, xshift=1.5cm + \blockXshift cm] {$\dim \, r$}; \node[below=1cm of x_n_space, xshift=0.75cm] {$\dim \, n - r$}; \node[below=1cm of x_n_space, xshift=0.75cm + \blockXshift cm] {$\dim \, m - r$}; % Draw the 0_n \coordinate (0_n_corner) at ($(left_center) + (-\cosBlockAngle, 0.25)$); \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngle:(left_center)}] \draw (left_center) rectangle (0_n_corner); \node at ($(left_center)!0.5!(0_n_corner)$) (O_n) {$\mbf{0}_{n}$}; \end{scope} % Draw the 0_m \coordinate (0_m_corner) at ($(right_center) + (\cosBlockAngle, -0.25)$); \begin{scope}[rotate around={\blockAngle:(right_center)}] \draw (right_center) rectangle (0_m_corner); \node at ($(right_center)!0.5!(0_m_corner)$) (O_m) {$\mbf{0}_{m}$}; \end{scope} \end{tikzpicture}
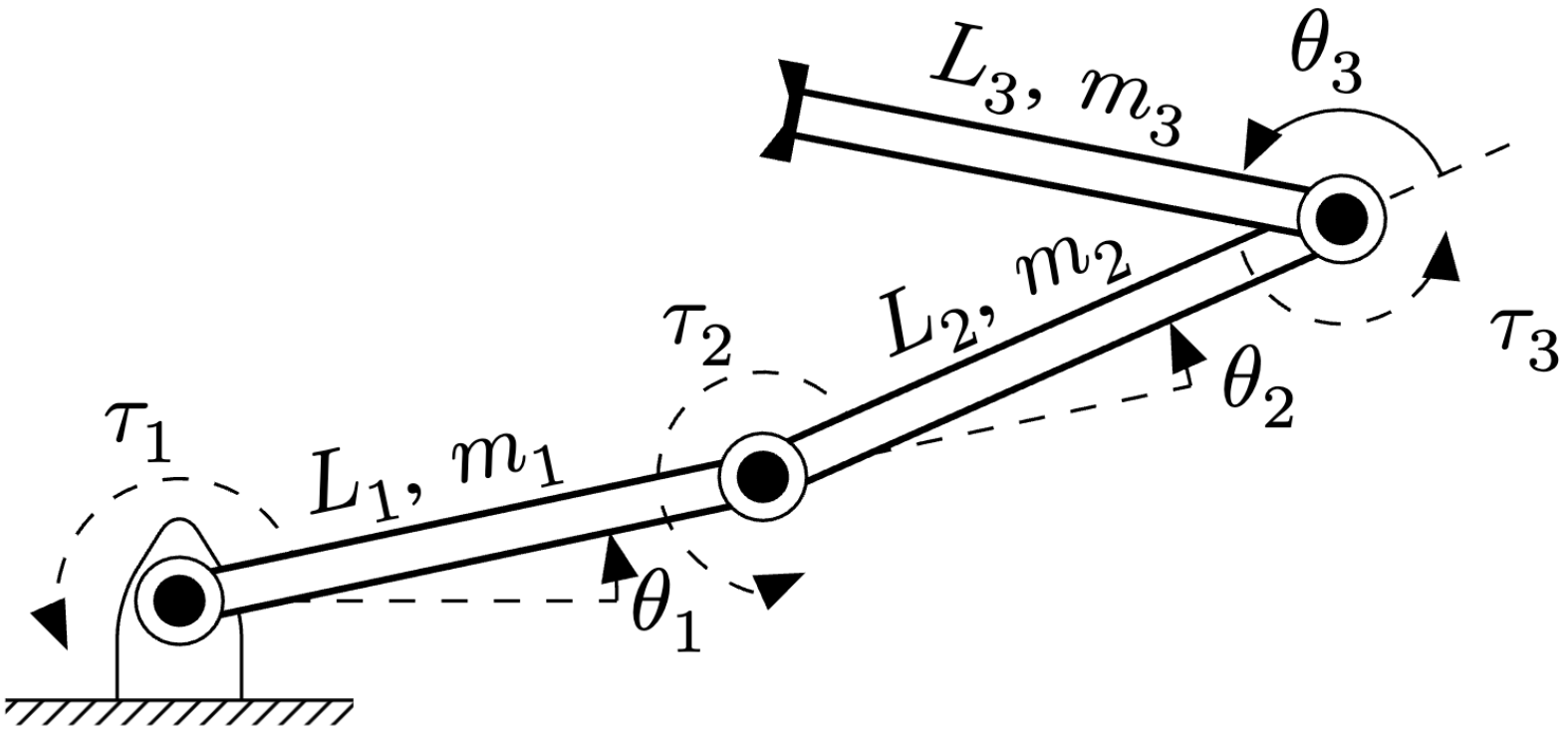
Three-Link Robotic Manipulator
-
-
Required Packages and Libraries:
\usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{patterns, arrows.meta}TikZ Code:
\begin{tikzpicture}[auto, node distance=2cm] % Modified from % https://texample.net/tikz/examples/three-link-annotated/ % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Constant Dimension Parameters % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define a variable as a length % Input: % 1 Variable name % 2 Value % % Example: % \nvar{\varx}{2cm} \newcommand{\nvar}[2]{\newlength{#1}\setlength{#1}{#2}} \def\arrowTipLength{2mm} % Length of arrow tip -> \def\arrowTipWidth{1.5mm} % Width of arrow tip -> % Define a constants for drawing \nvar{\dg}{0.2cm} \def\dw{0.25} \def\dh{0.4} \nvar{\ddx}{1.1cm} % Define the kinematic parameters of the robot \def\Lscale{1.5} \def\thetaone{12} \def\Lone{\Lscale*1.6} \def\thetatwo{12} \def\Ltwo{\Lscale*1.7} \def\thetathree{145} \def\Lthree{\Lscale*1.5} % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Objects and Styles % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Setting custome arrow style (uses package arrows.meta) \tikzset{ myarrow/.style = {->, -{Triangle[length=\arrowTipLength, width=\arrowTipWidth]}} } % Define commands for links, joints and such \def\link{\draw [double distance=1.5mm, thick] (0,0)--} \def\joint{ \filldraw [fill=white] (0,0) circle (5pt); \fill[black] circle (3pt); } \def\grip{ \draw[ultra thick](0cm,\dg)--(0cm,-\dg); \fill (0cm, \dg) -- +(0.5\dg, 0cm) -- +(0pt, -5.5pt); \fill (0cm, -\dg) -- +(0.5\dg, 0cm) -- +(0pt, 5.5pt); } \def\robotbase{ \draw[rounded corners=4pt] (-\dw,-\dh)-- (-\dw, 0) -- (0,\dh)--(\dw,0)--(\dw,-\dh); \draw (-0.7,-\dh)-- (0.7,-\dh); \fill[pattern=north east lines] (-0.7,-0.5) rectangle (0.7,-\dh); } % Draw an angle annotation % Input: % 1 Angle % 2 Label % Example: % \angann{30}{$\theta_1$} \newcommand{\angann}[8]{ \begin{scope}[black] \draw [dashed, black] (0,0) -- (#5*\ddx,0pt); \draw [myarrow] (#3*\ddx,0pt) arc (0:#1+#6:#3*\ddx+#7); \node at (#1/2-2:\ddx+#4)[yshift=#8] {#2}; \end{scope} } \newcommand{\jointTorque}[9]{ \begin{scope}[rotate=#6] \draw [myarrow,dashed] (#1,#2) arc (#3:#4:#5) node[midway, above, xshift=#8, yshift=#9]{#7}; \end{scope} } % Draw line annotation % Input: % 1 Line offset (optional) % 2 Line angle % 3 Line length % 5 Line label % Example: % \lineann[1]{30}{2}{$L_1$} \newcommand{\lineann}[7][0.5]{ \begin{scope}[rotate=#2, black,inner sep=2pt] \node[coordinate] (a) at (0,#1) {}; \node[coordinate] (b) at (#3,#1) {}; \path (a) -- node[black,rotate=#5,xshift=#6, yshift=#7] {#4} (b); \end{scope} } % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Start Drawing the Diagram % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % \robotbase \angann{\thetaone}{$\theta_1$}{1.6pt}{25pt}{1.6pt}{0pt}{-12pt}{-5pt} \lineann[0.1]{\thetaone}{\Lone}{$L_1$, $m_1$}{\thetaone}{15pt}{-1pt} \jointTorque{14pt}{0pt}{0}{180 + \thetaone}{14pt}{\thetaone}{$\tau_1$}{0}{-1pt} \link(\thetaone:\Lone); \joint \begin{scope}[shift=(\thetaone:\Lone), rotate=\thetaone] \jointTorque{12pt}{0pt}{0}{270}{12pt}{\thetatwo}{$\tau_2$}{4pt}{5pt} \angann{\thetatwo}{$\theta_2$}{1.6pt}{28pt}{1.6pt}{0pt}{-13pt}{-6pt} \lineann[0.1]{\thetatwo}{\Ltwo}{$L_2$, $m_2$}{\thetatwo + \thetaone}{15pt}{-1pt} \link(\thetatwo:\Ltwo); \joint \begin{scope}[shift=(\thetatwo:\Ltwo), rotate=\thetatwo] \angann{\thetathree}{$\theta_3$}{0.4pt}{-12pt}{0.75pt}{-15pt}{0pt}{0} \lineann[-0.7]{\thetathree}{\Lthree}{$L_3$, $m_3$}{\thetathree + \thetatwo + \thetaone - 180}{15pt}{-4pt} \draw [dashed, black,rotate=\thetathree] (0,0) -- (1.2\ddx,0pt); \jointTorque{12pt}{0pt}{0}{185}{12pt}{\thetathree}{$\tau_3$}{23pt}{-9pt} \link(\thetathree:\Lthree); \joint \begin{scope}[shift=(\thetathree:\Lthree), rotate=\thetathree] \grip \end{scope} \end{scope} \end{scope} \end{tikzpicture}
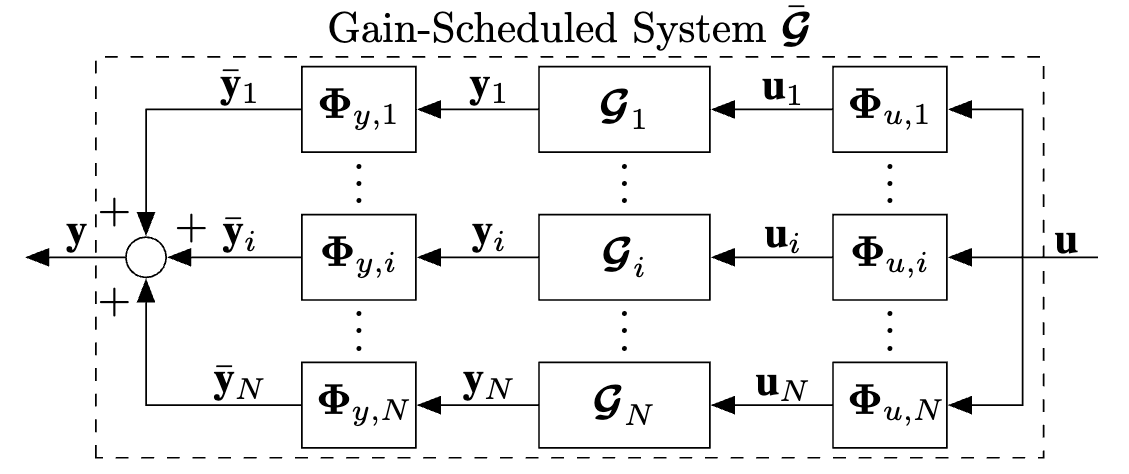
Gain-Scheduled System
-
-
Required Math Formatting Packages:
\usepackage{bm} \usepackage{amsmath} \usepackage{amssymb} \DeclareMathAlphabet{\mbf}{OT1}{ptm}{b}{n} \providecommand{\trans}{{\ensuremath{\mathsf{T}}}} \providecommand{\mbs}[1]{\ensuremath{\boldsymbol{#1}}}Required Tikz Packages and Libraries:
\usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{positioning, patterns, arrows.meta, calc}TikZ Code:
\begin{tikzpicture} % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Required Tikz Libraries % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % 1) arrows.meta is used for arrow tips % 2) positioning is used for relative positioning of nodes % 3) calc is used for coordinate calculations % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Constant Dimension Parameters % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % \def\blockWidth{4em} % Width of Control block \def\blockHeight{2em} % Height of Control block \def\blockVerticalSpacing{0.5cm} % Vertical spacing between parallel blocks \def\arrowTipLength{2mm} % Length of arrow tip -> \def\arrowTipWidth{1.5mm} % Width of arrow tip -> \def\smallArrowLength{1cm} % Length of small arrows used for input/output/scheduling \def\smallArrowStretch{1.5} % Stretch the length of the small arrows by this amount \def\dashedRectangleHeight{3.3cm} \def\dashedRectangleWidth{7.8cm} \def\dashedRectanglCenterXShift{4.5mm} \def\dashedRectanglCenterYShift{0.0cm} \def\parallelWidthStretch{3.4} % Stretch the width of the parallel blocks by this amount % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Objects and Styles % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Sum and multiplication nodes \tikzset{ sum/.style = {draw, fill=none, circle, node distance=1cm}, } % Control block \tikzset{ block/.style = {draw, fill=none, rectangle, minimum height=\blockHeight, minimum width=\blockWidth}, squareblock/.style = {draw, fill=none, rectangle, minimum height=\blockHeight, minimum width=\blockHeight, text width=\blockHeight, align=center}, } % Points \tikzset{ tmp/.style = {coordinate}, input/.style = {coordinate}, output/.style = {coordinate} } % Pin style to edge of block \tikzset{ pinstyle/.style = {pin edge={to-,thin}} } % Setting custome arrow style (uses package arrows.meta) \tikzset{ myarrow/.style = {->, -{Triangle[length=\arrowTipLength, width=\arrowTipWidth]}} } % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Start Drawing the Diagram % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Make the input node and the sum \node [input] (rinput) {}; \node [sum, right of=rinput] (sumSl) {}; % Make the parallel G1, Gi, GN blocks \node [block, right=\parallelWidthStretch*\smallArrowLength of sumSl.west](sumSl) (Gi) {$\bm{\mathcal{G}}_{i}^{}$}; \node [block, above=\blockVerticalSpacing of Gi.north, anchor=south] (G1) {$\bm{\mathcal{G}}_{1}^{}$}; \node [block, below=\blockVerticalSpacing of Gi.south, anchor=north] (GN) {$\bm{\mathcal{G}}_{N}^{}$}; % Draw the \vdots between G1 and Gi and Gi and GN \node [below=\blockVerticalSpacing/2 of G1, yshift=3pt, anchor=center] (vdots) {$\vdots$}; \node [below=\blockVerticalSpacing/2 of Gi, yshift=3pt, anchor=center] (vdots) {$\vdots$}; % Make the multiplication nodes across G1, Gi, GN blocks \node [squareblock, right=\smallArrowLength of G1.east] (sum1r) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{u, 1}$}; \node [squareblock, left=\smallArrowLength of G1.west] (sum1l) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{y, 1}$}; \node [squareblock, right=\smallArrowLength of Gi.east] (sumir) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{u, i}$}; \node [squareblock, left=\smallArrowLength of Gi.west] (sumil) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{y, i}$}; \node [squareblock, right=\smallArrowLength of GN.east] (sumNr) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{u, N}$}; \node [squareblock, left=\smallArrowLength of GN.west] (sumNl) {$\mbs{\Phi}_{y, N}$}; % Draw the \vdots between multiplication blocks \path let \p1 = ($(G1)!0.5!(Gi)$), \p2 = (sum1r) in node[yshift=3pt] at (\x2,\y1) {$\vdots$}; \path let \p1 = ($(G1)!0.5!(Gi)$), \p2 = (sum1l) in node[yshift=3pt] at (\x2,\y1) {$\vdots$}; \path let \p1 = ($(Gi)!0.5!(GN)$), \p2 = (sumir) in node[yshift=3pt] at (\x2,\y1) {$\vdots$}; \path let \p1 = ($(Gi)!0.5!(GN)$), \p2 = (sumil) in node[yshift=3pt] at (\x2,\y1) {$\vdots$}; % Make the node across the parallel G1, Gi, GN blocks \node [tmp, right=\parallelWidthStretch*\smallArrowLength - 6pt of Gi.east] (sumSr) {}; % Connect the blocks and the sum/mult nodes \draw [myarrow] (G1) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{y}_1$}(sum1l); \draw [myarrow] (sum1r) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{u}_1$}(G1); \draw [myarrow] (Gi) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{y}_i$}(sumil); \draw [myarrow] (sumir) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{u}_i$}(Gi); \draw [myarrow] (GN) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{y}_N$}(sumNl); \draw [myarrow] (sumNr) -- node[above, xshift=0.1cm, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{u}_N$}(GN); % Create a temp node to branch off from sumSr \node [tmp, left=\smallArrowStretch*\smallArrowLength - 25pt of sumSr.center] (tmp1) {}; % Draw parallel arrows to the RHS multiplication nodes \draw [myarrow] (tmp1) |- (sum1r); \draw [myarrow] (tmp1) -- (sumir); \draw [myarrow] (tmp1) |- (sumNr); % Draw parallel arrows from the LHS multiplication nodes and add + sign \draw [myarrow] (sum1l) -| (sumSl)node[at end, left, yshift= \arrowTipLength] {$+$}; \draw [myarrow] (sumil) -- (sumSl)node[at end, above, xshift= \arrowTipLength] {$+$}; \draw [myarrow] (sumNl) -| (sumSl)node[at end, left, yshift=-\arrowTipLength] {$+$}; % Label \bar{y} \draw [] (sum1l.west) node[above, xshift=-\smallArrowLength/2, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\bar{\mbf{y}}_1$}; \draw [] (sumil.west) node[above, xshift=-\smallArrowLength/2, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\bar{\mbf{y}}_i$}; \draw [] (sumNl.west) node[above, xshift=-\smallArrowLength/2, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\bar{\mbf{y}}_N$}; % Label u \draw [] (sumSr) -- (tmp1)node[at end, above, xshift=\smallArrowLength/2 - 4pt, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{u}$}; % Label y \draw [myarrow] node[at end, above, xshift=\smallArrowLength/2 - 2pt, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{y}$} (sumSl.west) -- ([xshift=-\smallArrowLength+5pt] sumSl.west); % Calculate the midpoint coordinates between G1 and GN \node [tmp, below= -\dashedRectanglCenterYShift of Gi.center, xshift=-\dashedRectanglCenterXShift] (sumSr)(center) {}; \draw[dashed] (center) ++(-\dashedRectangleWidth/2, -\dashedRectangleHeight/2) rectangle ++(\dashedRectangleWidth, \dashedRectangleHeight); \node[above, yshift=\dashedRectangleHeight/2 - 2pt] at (center) {Gain-Scheduled System $\bar{\bm{\mathcal{G}}}$}; \end{tikzpicture}
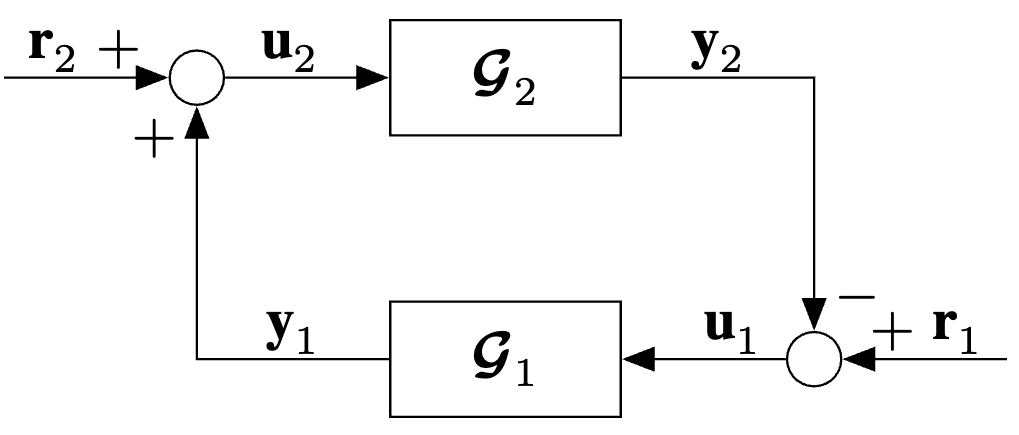
Negative Feedback Interconnection
-
-
Required Math Formatting Packages:
\usepackage{bm} \usepackage{amsmath} \usepackage{amssymb} \DeclareMathAlphabet{\mbf}{OT1}{ptm}{b}{n}Required Tikz Packages and Libraries:
\usepackage{tikz} \usetikzlibrary{positioning, patterns, arrows.meta}TikZ Code:
\begin{tikzpicture} % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Required Tikz Libraries % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % 1) arrows.meta is used for arrow tips % 2) positioning is used for relative positioning of nodes % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Constant Dimension Parameters % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % \def\blockWidth{4em} % Width of Control block \def\blockHeight{2em} % Height of Control block \def\blockVerticalSpacing{1cm} % Vertical spacing between parallel blocks \def\arrowTipLength{2mm} % Length of arrow tip -> \def\arrowTipWidth{1.5mm} % Width of arrow tip -> \def\smallArrowLength{1cm} % Length of small arrows used for input/output/scheduling \def\smallArrowStretch{1.5} % Stretch the length of the small arrows by this amount \def\smallArrowShrink{0.8} % Shrink the length of the small arrows by this amount % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Define Objects and Styles % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Control block \tikzset{ block/.style = {draw, fill=none, rectangle, minimum height=\blockHeight, minimum width=\blockWidth} } % Sum and multiplication nodes \tikzset{ sum/.style = {draw, fill=none, circle, node distance=1cm}, } % Points \tikzset{ tmp/.style = {coordinate}, input/.style = {coordinate}, output/.style = {coordinate} } % Pin style to edge of block \tikzset{ pinstyle/.style = {pin edge={to-,thin}} } % Setting custome arrow style (uses package arrows.meta) \tikzset{ myarrow/.style = {->, -{Triangle[length=\arrowTipLength, width=\arrowTipWidth]}} } % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Start Drawing the Diagram % ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ % % Make the Block \node [block] (Nonlinearity) {\(\bm{\mathcal{G}}_2\)}; \node [block, below=\blockVerticalSpacing of Nonlinearity.south, anchor=north](G) {\(\bm{\mathcal{G}}_1\)}; % Make temp nodes to draw input/output arrows \node [tmp, right=\smallArrowLength of G.east] (G_in) {}; \node [tmp, left=\smallArrowLength of G.west] (G_out) {}; % Draw the sum node at G_in \node [sum, left=\smallArrowLength of Nonlinearity.west] (sum_node_up){}; \node [sum, right=\smallArrowLength of G.east] (sum_node_down){}; % Draw input/output arrows between Nonlinearity and G \draw [myarrow](G) -| node[pos=0.25, above, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{y}_1$} (sum_node_up)node[at end, left, yshift=-\arrowTipLength] {$+$}; \draw [myarrow](sum_node_down) -- (G)node[at end, above, xshift=\smallArrowLength/2 + 5, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{u}_1$}; \draw [myarrow](sum_node_up) -- (Nonlinearity)node[midway, above, xshift=-3, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{u}_2$}; \draw [myarrow](Nonlinearity.east) -| node[pos=0.25, above, yshift=-0.09cm]{$\mbf{y}_2$}(sum_node_down)node[at end, right, yshift=\arrowTipLength] {$-$}; % Connect the disturbance to the RHS sum add + sign \draw [myarrow] ([xshift=\smallArrowLength+5] sum_node_down.center) -- node[above, midway, xshift=\arrowTipLength, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{r}_1$}(sum_node_down) node[at end, above, xshift=\arrowTipLength+3, yshift=-2] {$+$}; \draw [myarrow] ([xshift=-\smallArrowLength-5] sum_node_up.center) -- node[above, midway, xshift=-\arrowTipLength, yshift=-0.09cm] {$\mbf{r}_2$}(sum_node_up) node[at end, above, xshift=-\arrowTipLength-3, yshift=-2] {$+$}; \end{tikzpicture}